Blog
Would an EMR or an EHR work better for your practice?
EMRs and EHRs are highly valuable tools that has revolutionised clinic operations and benefitted healthcare professionals worldwide. It has become common practice for healthcare practitioners to adopt either Electronic Medical Record (EMRs) or Electronic Health Records (EHRs) or both.
Oftentimes, healthcare practitioners use the term Electronic Medical Reports (EMRs) and Electronic Health Records (EHRs) interchangeably. Essentially, Electronic Health Records (EHR) has overlapping similarities to what Electronic Medical Records (EMR) can do. Both systematically collect and store health information on patient electronically. However, there are nuance differences between EMRs and EHRs that contribute to why healthcare practitioners may choose one over the other.
Let’s find out more about EMRs & EHRs.
EMR vs EHR
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
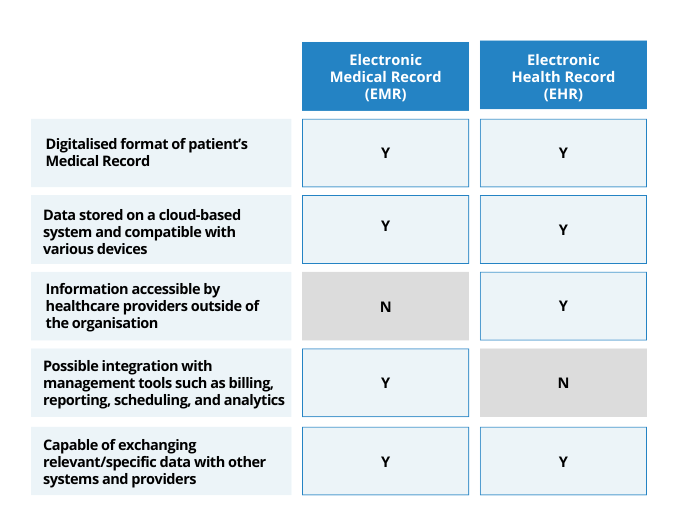
EMRs are digital versions of the detailed paper reports or charts recorded during the patients visit to the specific healthcare facility or clinic. EMR contains historical information collected during clinic visits such as patients’ appointment dates, clinical notes on condition and treatments, results for test conducted within the clinic, medicined prescribed and payment details. EMRs are usually not shared with other healthcare providers outside of the organisation. With the advancement of software & technology, EMRs are no longer just a digital repository of patient’s information and can be integrated with various management tools for scheduling, medication dispensation, billing and more. Additionally with the dataset collected enables the clinic to use analytics to gain greater insights into the clinics operations and map out visit journeys that enhances patient care, improve cashflow and elevate the success of the practice.
Electronic Health Record (EHR)
EHRs are also digitalised version of patient records however, information within an EHR is meant to be shared across authorised healthcare providers through network-connected, enterprise-wide information systems or other information networks and exchanges. Thus, information within an EHR may be more comprehensive with medical history collected from several healthcare providers that includes prescription track records, immunisation status, laboratory test results, radiology images and vital signs. EHR is particularly useful for doctors and healthcare practitioners during diagnosis and administering treatment as it allows them access to patients complete medical history. It also provides the healthcare community a platform to collaborate with one another.
Here’s a snapshot to summarise and visualise the difference between EMR & EHR.
NEHR & NGEMR
EHR & EMR has proven to facilitate better patient care for healthcare community and countries around the world are experimenting with adopting the use on EHR & EMR at a national level. If you are a doctor or a healthcare practitioner in Singapore, there are two nationwide healthcare programmes namely, National Electronic Health Record (NEHR) and Next Generation Electronic Medical Records (NGEMR) that is available. Although certain information collected between the 2 programmes are similar, its functions and purpose are not entirely the same.
The National Electronic Health Record (NEHR) was launched in 2011 to enable Ministry of Health (MOH) vision of “One Patient, One Health Record” with the aim of
- connecting healthcare professionals for care continuity,
- improving the quality of healthcare to achieve better health outcomes,
- increasing patient safety, and
- enhancing patient experience with seamless care.
It serves as a repository for key health information from various healthcare institutions, consolidating them into a holistic health record and is only strictly accessible to authorised healthcare providers in Singapore. Healthcare practitioners can view key health summaries within NEHR that includes allergies and adverse drug reactions, admission and visit history, discharge summaries, clinical and radiological laboratory results, history of past procedures, medication, and immunisation. Patients also have the liberty to access parts of their healthcare records in the NEHR via HealthHub.
In contrast, the Next Generation Electronic Medical Record (NGEMR) records the entire patient journey across different care settings, enabling patient-centric care and seamless care transition. On top of collecting vital medical information, NGEMR also consolidate administrative data on care delivery and patient care management capabilities. By unifying the EMR system across healthcare groups and providers, the initiative aims to do away with outdated standalone legacy systems and harmonise workflows, and seamless data transfer, and reports. NGEMR also boast features such as intelligent alerts and data analytical capabilities that help enhance patient journeys and supports better clinical decision making.
Similar to the NEHR programme, aggregated information will be available to patient providing patients with accessibility and more agency to their healthcare plans. This information would also be highly useful in providing valuable insights for medical education, research and population management that translated to better health outcomes.
(Source: Synpapxe –
https://www.synapxe.sg/healthtech/national-programmes/next-generation-electronic-medical-record-ngemr#nextgeneration)
Would an EMR or a EHR be more applicable for your practice?
That would depend on your clinic needs.
Generally, EMR is preferred for smaller scale practice or specialist who does not require extensive information for their patient’s treatment but prefers continuity and aligned communications within personnel across their clinic or organisation. With the possibility for integration with multiple management tools, EMR would be a perfect addition in creating a clinic environment that is seamless and organised.
However, there are also substantial benefits for healthcare practitioners to adopt EHR. Since EHR comprises of records collated from an extensive network of practitioners, this comprehensive information could come in handy in multiple ways like providing important information that might out of the clinic’s scope, minimising unnecessary screenings or duplication of previous treatment and facilitate a collaborative environment between the healthcare community and patients.
A report produced by the Global Observatory for eHealth states a number of advantages to adopting EHR that includes,
- Improving the quality, accuracy, and timeliness of patient information at the point of care.
- Highlights areas of concern and health services delivery and providing insights into health care costs, utilisation, and outcomes.
- Promotes quality of care, reduce costs, support patient mobility, increase reliability of information, and provide access to patient information to multiple health care providers.
EHR also promotes voluntary collaboration with other healthcare practitioners by contributing information that might be useful for medical research that improves medical decision-making and provide better patient outcomes across the board.
At Galen Health, we want to help ensure that your clinic can function at the optimal level hence we have built a Clinic Management System that can support your clinic needs holistically. Whether you would like to maintain your independently or want to be part of Singapore Healthcare initiatives, we are here to provide you with the right solution. Galen Health CMS is both NEHR and NGEMR ready and features various modules like Chronic Disease Management, Claims Management and more.
Speak to our dedicated team to learn how we can help you streamline your practice and achieve your clinic goals.


